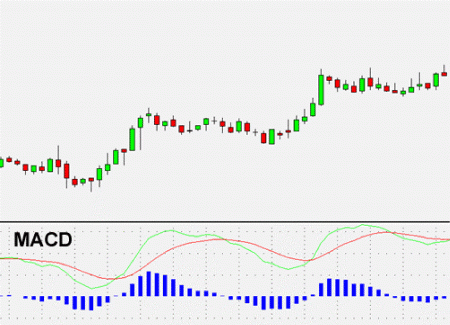
Moving Average Convergence-Divergence Definition. Moving Average Convergence-Divergence, or “MACD”, is a common technical indicator used by forex traders to detect and confirm trends in price behavior of their target currencies. It is a lagging indicator as it reacts after a trend has formed. The MACD uses two different exponential moving averages of prices. Parameters are variable, but the typical settings are 26 days or periods for one EMA and 12 days or periods for the other EMA. The “fast line” is then the moving average of the difference of these two lines. A “slow line” or “signal line” is the moving average of the difference between the “fast line” and a 9 day or period EMA. Occasionally, a bar chart called the MACD histogram may be added to visually indicate entry and exit signals. The chart below illustrates how the MACD looks and operates. Forex traders look for crossovers of the two lines as a signal of a bullish or bearish trend. When the “green line”, or MACD, diverges from the “red line”, or signal line, the indicator is signaling overbought and oversold conditions, respectively. The MACD is often used in combination with a leading indicator, typically the RSI or Reserve Strength Index, to confirm a signal before entering a trade position.
Forextraders' Broker of the Month
BlackBull Markets is a reliable and well-respected trading platform that provides its customers with high-quality access to a wide range of asset groups. The broker is headquartered in New Zealand which explains why it has flown under the radar for a few years but it is a great broker that is now building a global following. The BlackBull Markets site is intuitive and easy to use, making it an ideal choice for beginners.